There are three approaches used widely to import Excel into InDesign. And then there is Pagination.
Let’s see their differences and how to use them.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
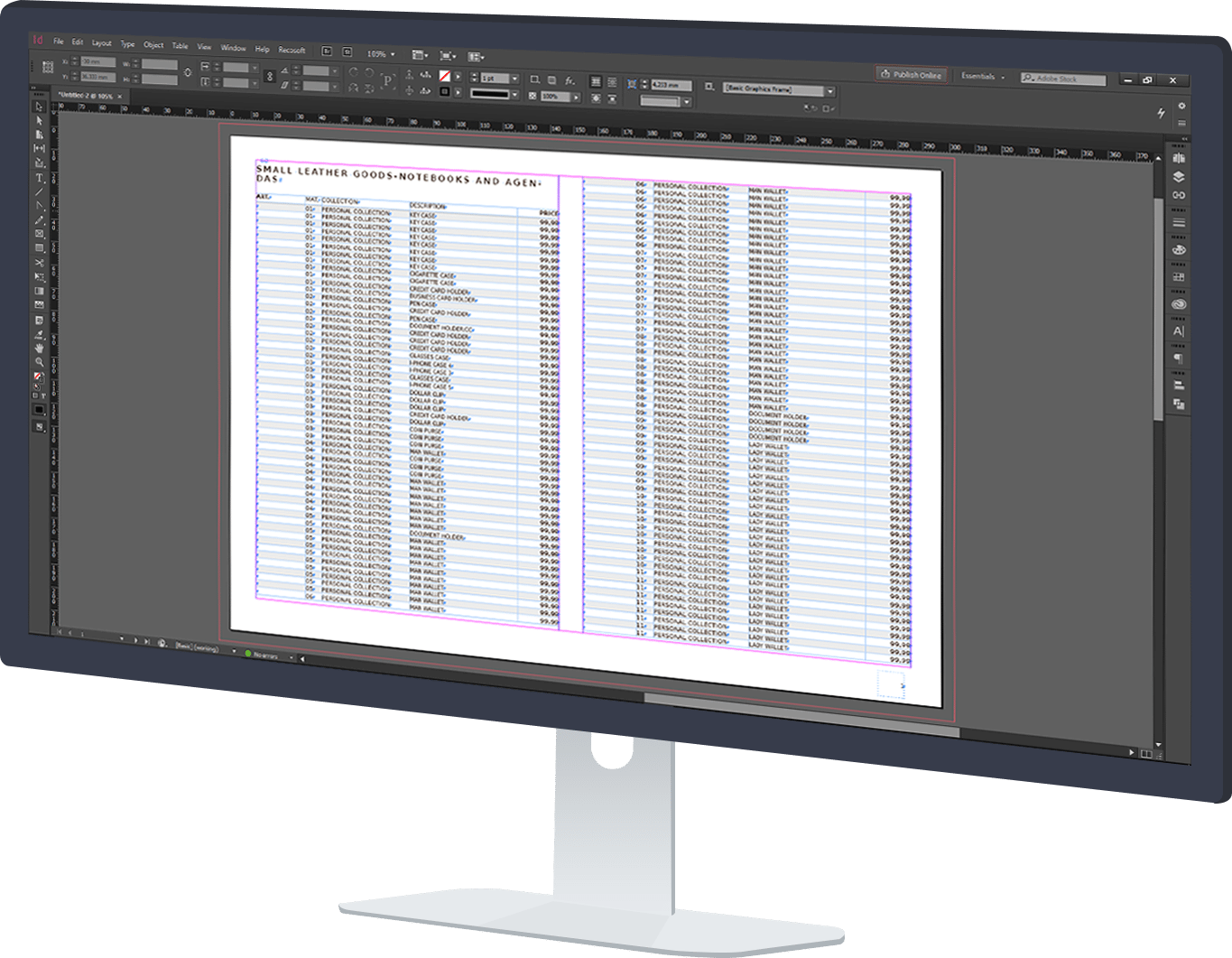
The Place command is a method of importing data from a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet to an Adobe InDesign document. It can be used with Excel and InDesign tables to paginate documents such as simple price lists and business cards. However, Place command options are best used in the population and updating of product sheet tables, since one of the features that this method offers is the creation and maintenance of the links between spreadsheet files and the InDesign document.
The Place command has a relatively limited feature set. This restricts its application to projects with only the most simple requirements. Check how Pagination combines the Place command’s ease of use with a much broader range of possibilities.
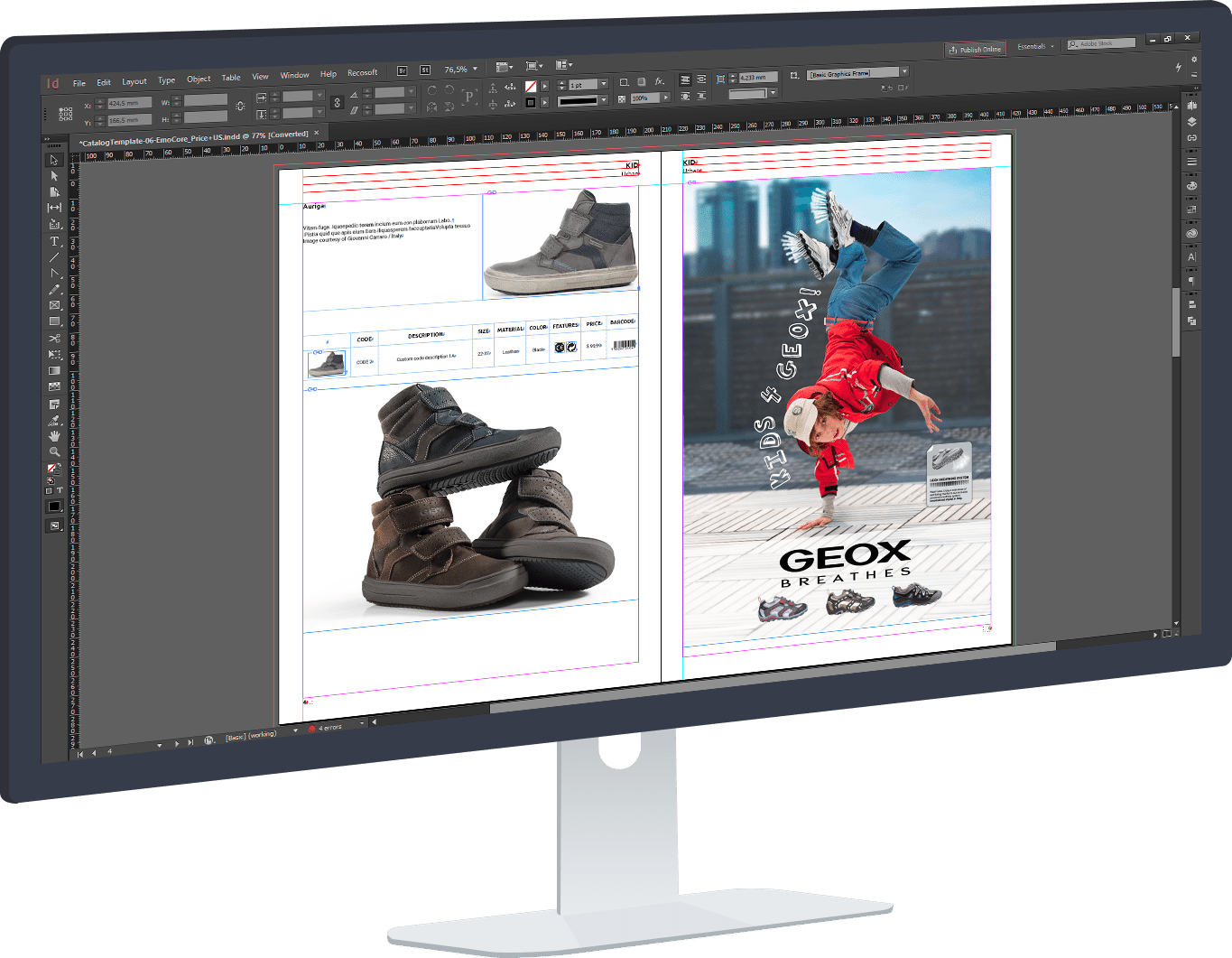
InDesign Data Merge is the most common method to import Excel into InDesign.
It can be used for paginating spreadsheets into business card batches, yearbooks, certificates, price lists and product sheets.
One of InDesign Data Merge’s main weaknesses is the need to prepare spreadsheets to InDesign’s exact import specifications. Only .csv and .txt files can be imported, and the conversion process can be daunting, complex, and prone to errors. Check how Pagination offers solutions that eliminate the need for conversion and significantly extend the Data Merge tool’s overall feature set.
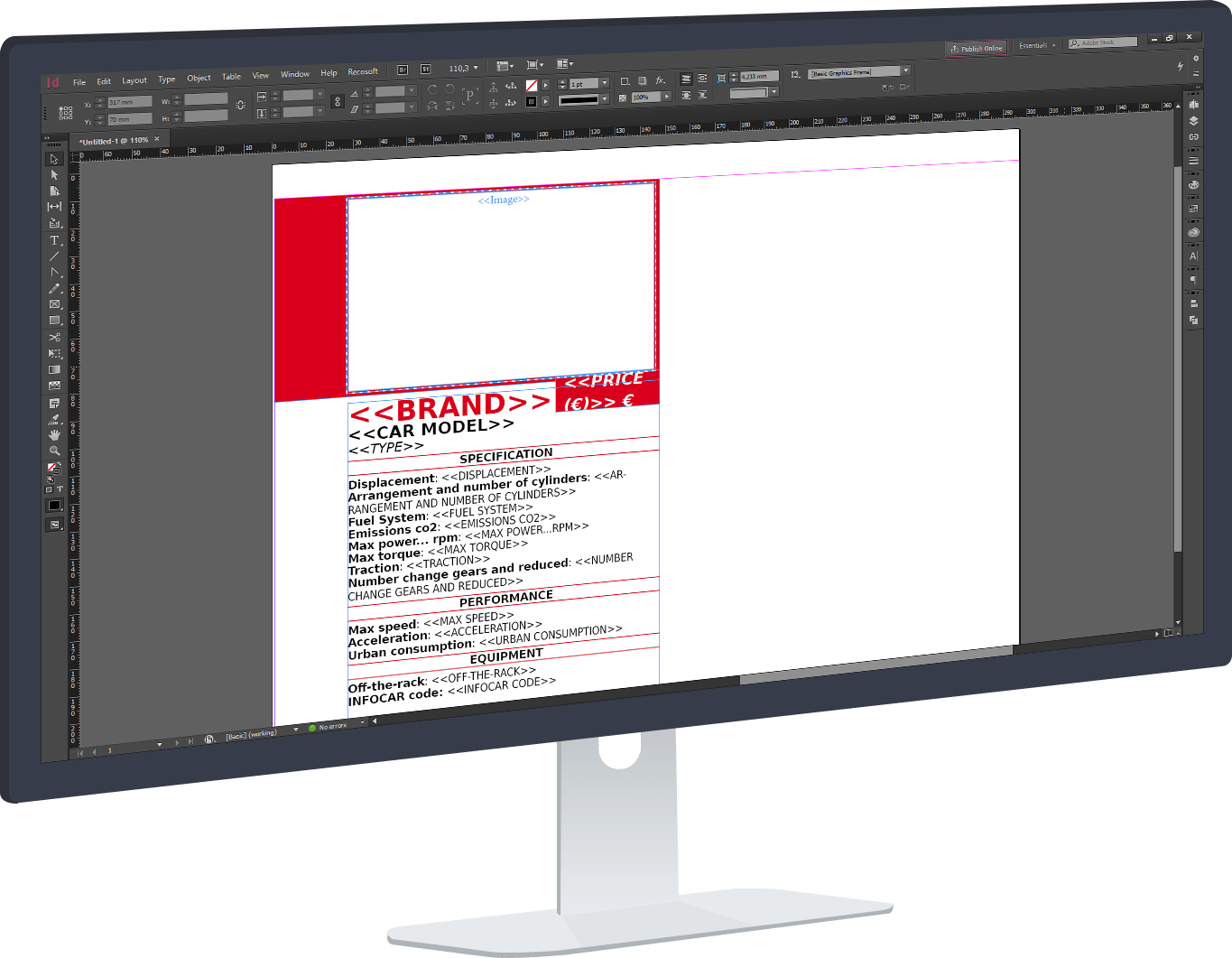
Another method to import Excel into InDesign is InDesign XML Import. It requires you previously converted your Excel file to XML format. Importing XML files into InDesign enables you to automate almost any kind of layout. Text, graphics, attributes, and tables can all be used to create complex documents such as calendars, multi-hierarchy price lists, and technical catalogs. Pairing an XML import with JavaScript provides even more layout and automation possibilities.
InDesign XML Import requires a steep learning curve, and a dedicated team can be required to establish, maintain and troubleshoot the logic behind even relatively simple operations. This high barrier to entry and long-term resource commitment should be considered before using XML on any challenging database publishing or variable data printing project. Discover how Pagination offers the same high customization levels as XML but with far greater ease of use.
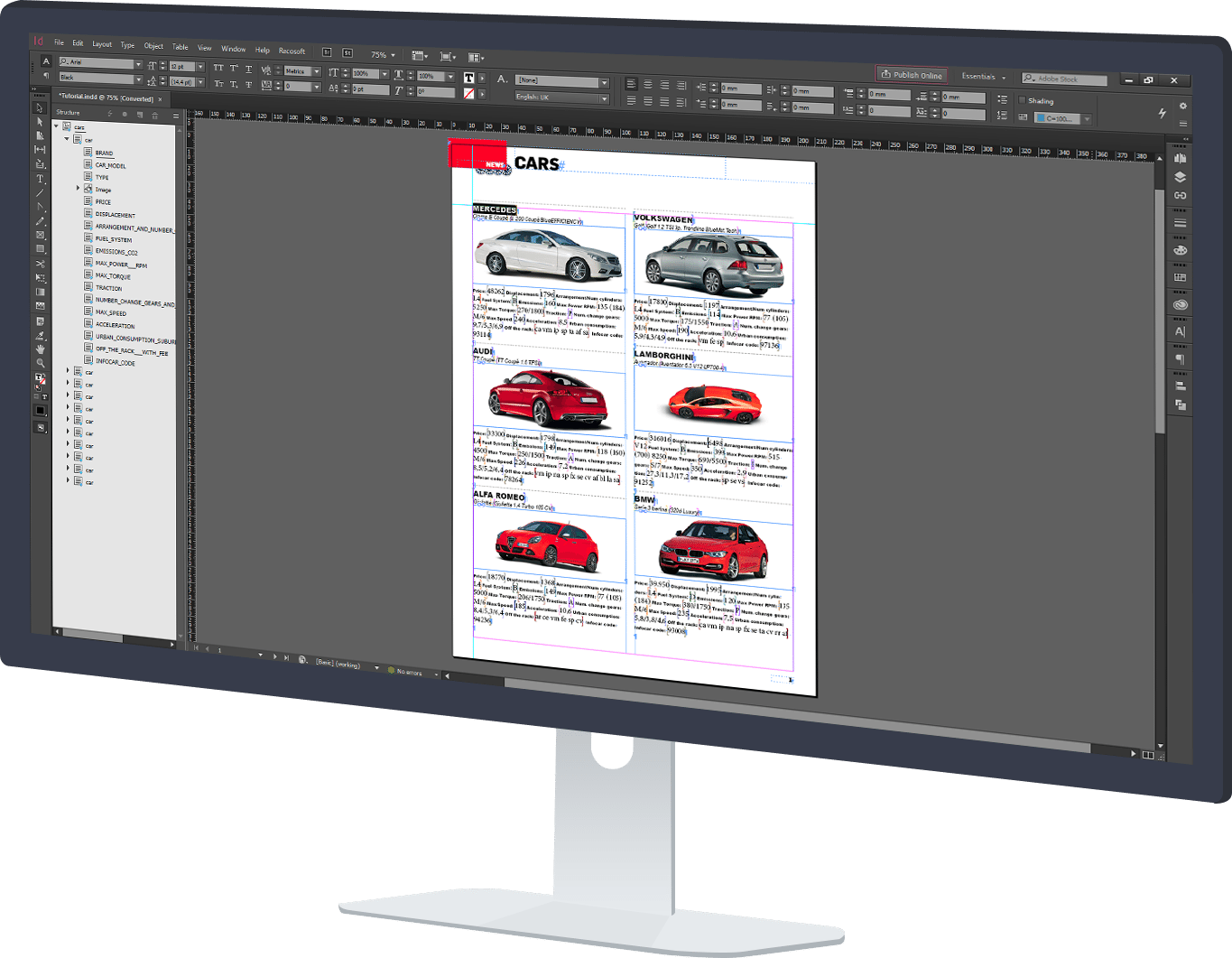
Pagination is a cloud database publishing service that allows you to create, within seconds, documents in PDF and InDesign from any kind of data source, such as Excel, CSV, MySQL, XML, or exports from corporate databases. The speed and ease of use (you do not need any kind of initial training) have made it one of the world’s most popular tools, used by marketing teams and advertising agencies to develop their own publishing projects. Pagination does not require installation; you can access it from any device, any browser or operating system anywhere and at any time. It’s commonly used to create catalogs, price lists, circulars, product sheets, and look books from all types of documents whose information resides in a database or in one or more spreadsheets.
Use one of our free InDesign Templates or upload your own layout. Create documents anytime and from anywhere.
![]()
Change language
Manage Cookie ConsentTo provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Functional Functional Always activeThe technical storage or access is strictly necessary for the legitimate purpose of enabling the use of a specific service explicitly requested by the subscriber or user, or for the sole purpose of carrying out the transmission of a communication over an electronic communications network.
Preferences PreferencesThe technical storage or access is necessary for the legitimate purpose of storing preferences that are not requested by the subscriber or user.
Statistics StatisticsThe technical storage or access that is used exclusively for statistical purposes. The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for anonymous statistical purposes. Without a subpoena, voluntary compliance on the part of your Internet Service Provider, or additional records from a third party, information stored or retrieved for this purpose alone cannot usually be used to identify you.
Marketing MarketingThe technical storage or access is required to create user profiles to send advertising, or to track the user on a website or across several websites for similar marketing purposes.